Psoriasis (also known as lichen planus) is a chronic, non-infectious and often relapsing skin disease.
Psoriasis, the symptoms of which determine a tendency to damage the peridermal tissues, manifest as scaly papules, in addition, it should be noted that this disease is one of the most common skin lesions, occurringall ages.
The etiology of this disease is still not fully researched and proven, however, many dermatologists still agree that psoriasis is a disease directly related to inherited genetic diseases.
Do not self-medicate. At the first sign of illness, see your doctor.
general description
Psoriasis is characterized by duration and persistence of its own course. Meanwhile, his departure, which could last several months or years, indicates a subsequent return and the length of his life span. Spontaneous cure of this disease is extremely rare.
If you try to identify a specific group of people who are predisposed to the onset of psoriasis, the solution will not be obvious. The fact that psoriasis, acting as a systemic process, develops not only in people with real immune disorders, but also in people with certain functional or morphological disorders related tofunctions of different systems and organs.
Regarding the group of dermatological diseases, psoriasis is one of the most studied among them. Meanwhile, no theory that exists to this day can fully determine the nature of this disease. Thus, matters concerning his therapy and prevention are both uncertain and, at the same time, acute, as before. Depending on the specific time period, various opinions have been proposed regarding the origin of psoriasis. This led to the selection of several forms, each based on the results of several laboratory studies and clinical observations.
- Inheritance of the disease. This implies the presence of psoriasis in the framework of several generations in which cases have been reported. By the way, heredity is considered the main and reliable cause of the development of psoriasis (in this case, psoriasis increases under the influence of various provoking factors).
- Metabolic nature of the disease. In this case, dysregulation of fat metabolism (i. e. cholesterol metabolism), decreased incidence during starvation, increased phosphorus levels in psoriasis, etc. v. is considered.
- Viral nature of the disease. In this case, the concept of a direct association of viral infection with the etiology of the disease under consideration was formed on the basis of long and numerous clinical observations. Accordingly, for the same reason, the infectious (and also viral) nature as a theory of the development of psoriasis is the most ancient. Thus, the end of the 19th century was marked by cases of the formation of very broad groups of psoriasis, formed against the background of patients suffering from such diseases as scarlet fever and influenza. The systemic nature of the actual lesion, its recurrence and persistence, the presence of a relationship with meteorological and geophysical factors, as well as a number of features inherent in its developmentThe characteristic rash of psoriasis also serves as confirmation of the infectious nature of the disease. For the time being, a search is currently underway for viral agents through which the psoriasis process can be triggered.
- Endocrine nature of the disease. The theory of a direct link between the onset of psoriasis and the endocrine (as well as metabolic) nature has in the recent past been widely supported. When examining patients with psoriasis, certain disorders of the endocrine scale are often revealed, which is considered the reason for the relevance of such an association. In particular, disorders related to the inherent functional state of the gonads, the effects of the menstrual cycle, pregnancy, childbirth and lactation, the type of marked changes detected in the studyon the patient's pituitary-adrenal system was emphasized.
- The neurological nature of the disease. It consists of the onset of the disease against the background of an actual neurological shock that occurs to the patient (more precisely, after it has been transferred). In about 30% of cases, exacerbations of the disease occur precisely on the basis of stress. In this case, the patient has a reduced tolerance to the effects of stress and its consequences. At the same time, the disorders they suffer from (asthenia, vegetative-vascular-organ, vegetative-vascular-dystrophic, and asthenic) combined with neural responses that stimulate the formation or even causeexacerbating the characteristics of the current vicious circle.
Classify
As we have already noted, psoriasis acts as a chronic and relapsing disease. Any of its existing forms can be attributed to one of the variants of the psoriasis-associated classification, which has a distribution for pustular or non-pustular psoriasis. In general, the classification is as follows:
- Pustular psoriasis
- systemic psoriasis;
- globular psoriasis (squamous pustular disease);
- palmoplantar psoriasis (extremity psoriasis, persistent palmoplantar psoriasis, barbera pustular psoriasis);
- chronic form of persistent dermatitis (psoriasis of the soles and palms, psoriasis of the palms);
- herpetiform psoriatic impetigo.
- Non-pustular psoriasis
- psoriasis vulgaris or psoriasis vulgaris, psoriasis simple (plaque, stable psoriasis in chronic form);
- erythrodermic psoriasis (erythrocytic psoriasis).
Some authors adhere to the need to supplement this classification, so that types or forms of psoriasis can be added to it in the following variations:
- seborrheic psoriasis (seborrheic psoriasis);
- Psoriasis of napkins;
- drug-induced psoriasis;
- "Reversible psoriasis" (psoriasis of the skin folds, superficial flexors).
Psoriasis: symptoms
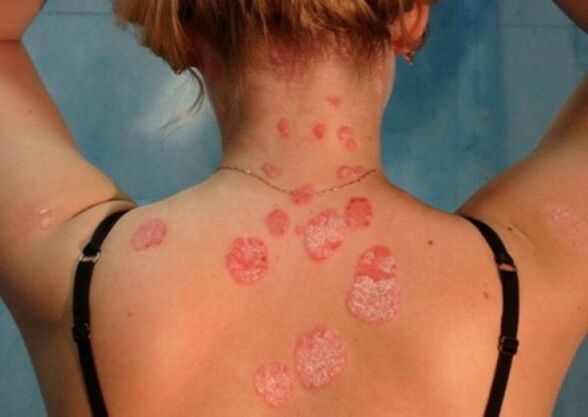
The first symptom of psoriasis is a papule-like rash, which is characterized by a gradual increase along the periphery, and their transformation into papules and vesicles and fusion of each other. thus appearing arrays of different sizes. The development of psoriasis in the skin defines three main stages for it.
First stage
This stage is defined as an advanced stage, it is caused by new skin formations (actually papules), as well as an increase in the size of already existing skin formations. This is also accompanied by the formation of an erythematous border around the lesion (such a border is defined as a peripheral growth zone). Plaques along the edges are not prone to flaking, while peeling, which serves as the final stage of the inflammatory process, has not kept pace with the growth of the forming psoriasis.
Second stage
The second stage defines a stationary period in which new elements do not appear, however, existing elements in the form of arrays and papules do not change in size. In general, the appearance of papules can be completed in any of the stages, so the stationary phase may be accompanied by the simultaneous appearance of papules, vesicles, and papules. Let us explain what are the three types of papillomas listed. Thus, papules are elements of a circular skin rash with an inner diameter of 15-20 mm (for this reason, these papules are also called coin-shaped). In turn, vesicular papules are elements of the rash, flat or convex, oval or round, resembling lentils. And finally the millet, which has a cone shape of particles and is therefore similar to a hemp seed. Basically, these papillomas are small in size, the predominant area being near the hair follicle.
The third stage
This phase is a reversal (or retracement). Its main feature is that the rash gradually disappears, and a white border of the pseudo-circular pattern is formed around the rash itself (it is defined as Voronov's rim). During this stage, some patients may experience mild itching. As for any subjective sensations, they are expressed almost insignificantly, or even completely, at all.
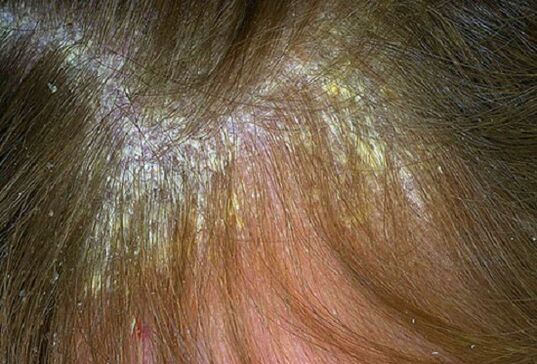
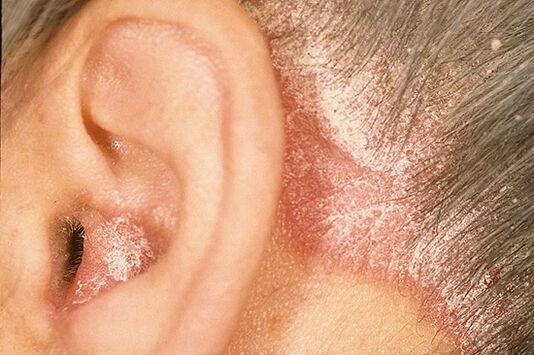
Rashes may be noted in any area of the skin, however, they are mainly localized to the superficial areas of the flexors of the limbs, especially the elbows and knees, the sacral region, scalp (here, in particular, the area along the growing edge of the hair is distinguished, identified as the "Psoriasis Crown"). Psoriasis on the head, the symptoms of which, although determined by the severity of their own manifestations, do not lead to a change in the structure of the hair, as well as their loss.
As for the concentration of plaques in the extensor surfaces of the knee and elbow joints, here they often persist for a long time from the time of the general rash (this feature defines them as "meaning" plaques). service"). Some patients are faced with the fact that skin folds in the inguinal-femur region or mammary glands, as well as in the axillary glands, and often such a lesion can be isolated.
Unpleasant psoriasis
It develops against the background of active skin exposure to pre-existing advanced psoriasis of certain irritants, especially sun rays or specific ointments, as well as other types of substances. Other irritation affects the plaques. These patches, in turn, become more convex, the color changes to cherry red, a superheated belt forms in the surrounding area, so that the sharp boundaries become blurred. This belt, after the resolution of plaque, has a wrinkled appearance.
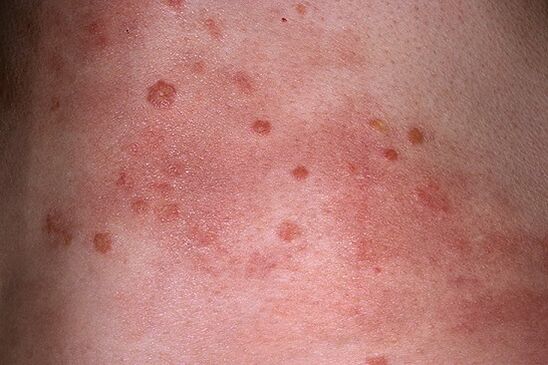
Spotted Psoriasis
This form of the disease presents as mild infiltration (under the general definition, infiltration is the infiltration of tissues by one or another substance) from the elements of the rash. In turn, they look like spots (not papules). Spotted psoriasis develops according to a pattern, according to a rule, and also has similar characteristics to sepsis. As the main method of distinguishing the disease, the definition of the correspondence of the disease process with its characteristic psoriasis triad is used.
Old Psoriasis
This form of the disease can be viewed in terms of symptoms in the form of severe lateral infiltrates of the plaques, their general cyanosis, with a hyperkeratosis or wrinkled surface. This type of foci is particularly difficult to cure, and their future transformation into malignancies is not excluded (this happens infrequently, but unfortunately, it is not necessary to exclude this option).
Seborrheic Psoriasis
This form of psoriasis, as the name implies, develops in patients with their associated seborrhea. The disease manifests from the scalp, in the posterior region of the edges, on the chest, in the nasolabial folds, in the subnasal nodes and in the scaly parts of the back. Emerging psoriasis scales have a strong capacity to saturate with sebum, so that they stick together and lie within the plaque surface, thereby allowing the disease to mimic the characteristic pattern of seborrheic eczema.
Palmar-plantar psoriasis
The disease may present as common psoriatic plaques and papules, or as hyperkeratosis that mimics calluses and calluses. In some cases, psoriasis on the hands, the symptoms of which are noted in this case are on the palms (or on the legs - by definition, on the soles of the feet) continuously, manifesting as increased thickeningor horny. . The boundaries of this type of lesion are characterized by clarity; In rarer cases, this form of psoriasis is limited to the appearance of large ring sloughs.
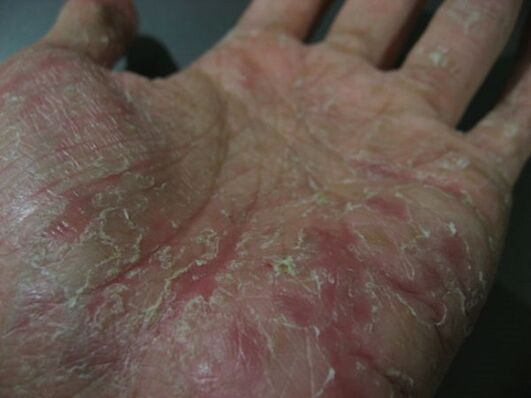
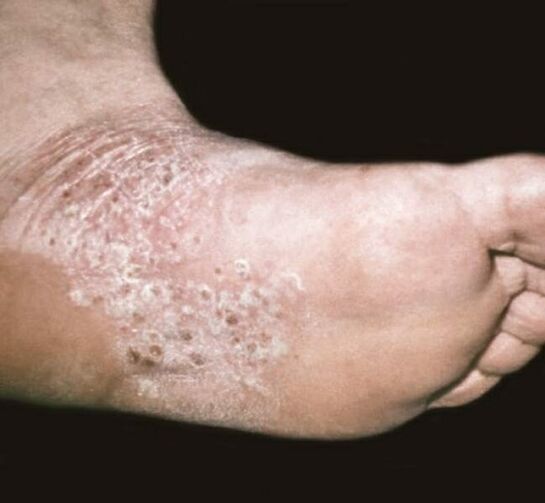
Exudative psoriasis
This form of psoriasis is characterized by the severity of excessive secretions in an inflammatory response; It occurs in the advanced stages of psoriasis. Going to the surface of the scab, the exudate provides saturation of the accumulation of scales, thereby forming from them shapes that look like crusts. These elements are minor, identify them as crusts, the color of these elements is slightly yellow. After their removal, the surface may be exposed to bleeding and oozing vapors. The flakes, when dry and layered, often form a kind of large, oyster-shell-like agglomeration (this has been identified as ruptured psoriasis).
Intestinal psoriasis
Intestinal psoriasis, whose symptoms come on suddenly, is characterized by the formation of multiple spots on the skin. The disease is mainly diagnosed in patients aged 8 to 16 years. Often, a strep infection serves as a precursor to teardrop psoriasis.
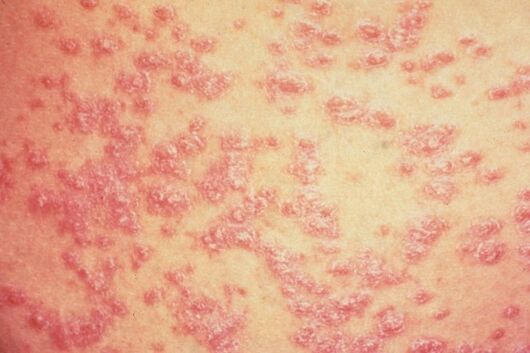
Psoriasis of the nails
Psoriasis of the nails, the symptoms of which provide the isolation of this type of psoriasis in three main forms, depending on the extent of damage to the nail, it can be atrophy, point or hypertrophic.
Perforation lesions are considered to be the formation of indentations on the nail plates, which can also be compared to the surface of the pinhole. The manifestation of this form of psoriasis can be in a slightly different version, in its characteristics, similar to onychomycosis. In this case, in the free margin, the nail changes color, becomes dull, easily crumbles without much effort. As a sign that can distinguish psoriasis, an inflammatory border is formed along the periphery of the affected nail area. It is presented as the edge of a piece of paper in the nail, visible through the nail plate.
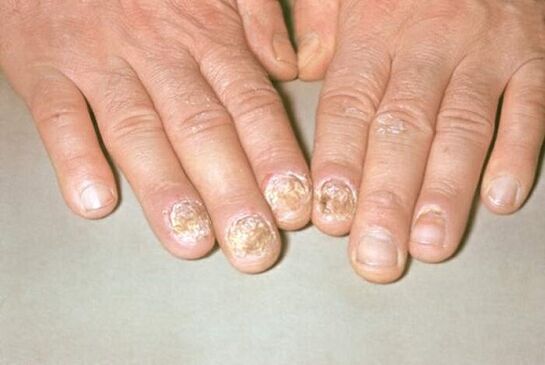
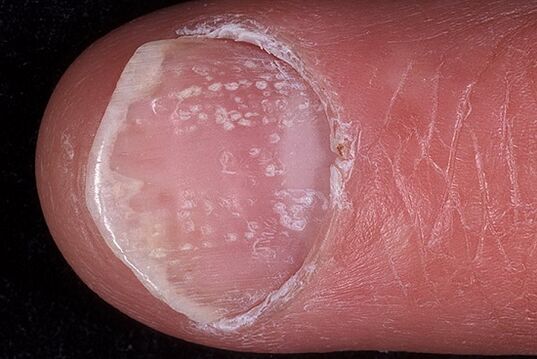
Psoriatic arthritis (psoriatic arthritis)
Psoriatic arthritis, the symptoms of which is manifested by infiltrates, involves the periarticular tissues with concomitant damage to the joints, mainly affecting the intervertebral joints. Meanwhile, the possibility of involvement of large joints in the pathological process cannot be excluded; The joints and joints of the sacroiliac spine are extremely rarely at risk for this problem.
It is important to note that psoriatic arthritis, unlike other types of arthritis (which by general definition means arthritis), is formed against the background of an already existing psoriatic rash in the patient, usuallyassociated with nail damage. . In addition, an important point that can be distinguished is that the onset of this type of arthritis is associated with an exacerbation of cutaneous psoriasis, which in most cases is characterized by an exudate.
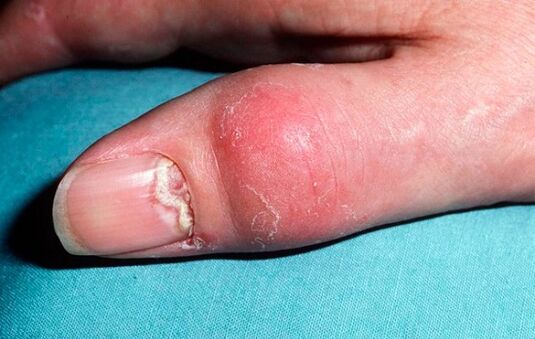
Inappropriate treatment of the disease during the progression of the disease is often accompanied by a non-specific response of the body. It is allergenic in nature and consists of the appearance of redness in the area unaffected by the psoriatic plaques, this redness, which merges, affects the skin completely. This process is associated with an elevated temperature (in the range not higher than 39 degrees), as well as an increase in lymph nodes, a feeling of tightness in the skin, burning and itching. In frequent cases, the nails are also heavily peeled, thickened and scaly, hair loss. This image has shown the involvement of erythrodermic psoriasis. Erythroderma ends with restoring the traditional version of the psoriasis process.
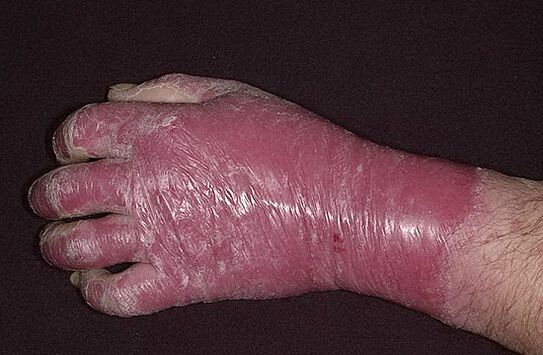
In general, disease recurrence occurring in the autumn-winter as well as the spring-summer is an important factor to be borne in mind, even when prescribing necessary treatments.
Treatment of psoriasis
Before the appointment of treatment, a thorough examination of the patient is carried out and specific measures have been identified, which are based on the stage of the disease process, on its clinical variety, the general condition of the patient, the presence of comorbidities, the concordance of the manifestations of the disease with the seasonality, etc. v. the fastest, and at the same time, achieve favorable treatment results in the case of uncomplicated forms of psoriasis with their short course, as well as with limited manifestations. In general, the treatment of psoriasis is a rather laborious process, and in most cases, complete cure is not possible - the disease simply regresses (that is, a period that persists withoutsymptom onset), however, is also a positive outcome for it.
The primary goal of treatment has been determined to be to minimize symptoms that may be associated with the addition of preventive measures.
First of all, with psoriasis, a diet is prescribed, in which foods that aggravate the disease (spicy foods, chocolate, alcoholic beverages) are excluded from the diet. Restrictions also apply to the consumption of smoked meats, honey, fried and fatty foods, etc. v. During an exacerbation of the disease, it is advisable to eat a lot of fruits and green vegetables (except for those with a red color: apples, tomatoes, cherries, etc. ), fish and lean (boiled) meat.
Psoriasis treatment is useful in treating the disease in terms of hygienic resort facilities. Taking into account the particular sensitivity of the skin in psoriasis patients, exposure to direct sunlight should be avoided between 11am and 4pm.
As for the drug treatment of psoriasis, it is based on the use of several methods. First of all, there are external agents (topical creams, ointments. . . ), systemic drugs (injections, oral drugs. . . ) and methods such as phytotherapy, physical therapy. , … external treatments. In particular, the following drugs are most commonly used among them:
- Salicylic ointment. With its help, the softening of the already formed flakes is ensured, which, in turn, gives the possibility of their early removal along with better absorption of other drugs. This ointment (0, 5% or 5%) is applied to the affected skin areas in a thin layer, 1-2 times a day. An important feature of the application is the use of a small amount of an ointment with a significant inflammatory property (that is, the more obvious the degree of inflammation in terms of the nature of its manifestation, the greater the amount of ointment used forthe less it is). Salicylic acid, which acts as the drug's base, is also found in some other ointments used in the treatment of psoriasis.
- Sulfur tar ointment (5 or 10%). The use of this ointment helps to reduce inflammatory processes associated with the skin. Contraindications to use are exudative psoriasis (i. e. psoriasis, accompanied by scaly and exudative scales). You can not apply this ointment to the skin of the face. Tar shampoo is used to treat scalp psoriasis.
- Naphthalene ointment. It is used to treat the regressive and stationary stages of the disease. The outbreak or progression of psoriasis determines the unacceptable use of this remedy. With the help of this ointment, intense itching and inflammation are reduced. 5% or 10% ointment is used.
- Glucocorticosteroid drugs. Their use helps to reduce the intensity of inflammation. They are used only in short courses with the mandatory supervision of a specialist.
- Ointments contain vitamin D. Such ointments have an anti-inflammatory effect, and at the same time improve the course of the disease.
As for systemic treatment, it is strictly selected individually and only by the attending physician. As noted, it means using a variety of pills, injections, etc. v.
Phytochemotherapy is a treatment for psoriasis that involves shining ultraviolet light on the affected areas of skin. For this, a special type of installation is used, irradiating such areas without affecting healthy skin.
In general, the treatment of psoriasis can have many different programs implemented in practice, but none of these programs are generally accepted due to differences in their regimens and specificities. , so the effectiveness of any program cannot be determined equally for all patients. Let us reiterate that the treatment of the disease is carried out on a strictly individual basis under the constant supervision of the attending physician.
If symptoms suggestive of psoriasis appear, contact a dermatologist and infectious disease specialist.























